Current Energy-Efficient Water Dispenser Market: Hidden Concerns and Structural Challenges Beneath the Prosperity
1. Market Application: A Polarized Landscape of Public Necessity vs. Household Absence
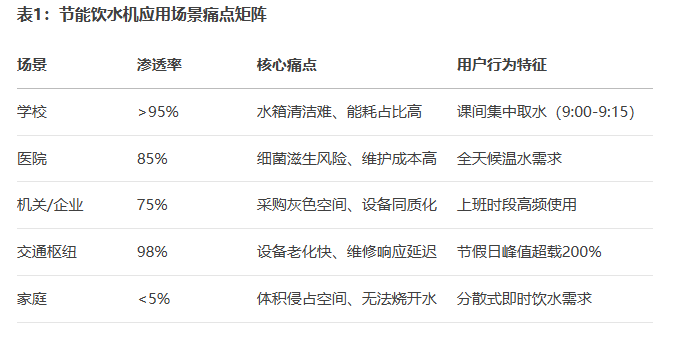
Energy-efficient water dispensers have become standard infrastructure in the public sector, with their distribution deeply aligned with Chinese drinking water culture:
- Education System: Covering over 90% of primary, secondary schools, and universities nationwide; a single unit serves over 100 people per day on average.
- Medical Institutions: Class III Grade A hospitals deploy an average of 52 units per campus, yet insufficient tank cleaning frequency raises hygiene concerns.
- Government/Enterprise Units: Account for 75% of public drinking water equipment; dependence rate in government building water stations reaches 98%.
- Transport Hubs: Coverage in high-speed rail stations reached 98% nationally in 2024; Beijing South Station records a single-day water intake of 12 tons.
Conversely, household market penetration remains below 5%, as traditional models are rejected due to bulky size and complex installation requirements.
2. Competitive Landscape: Homogenization Quagmire and Profit Erosion
The industry is trapped in a vicious cycle of “technological stagnation → overcapacity → price wars”:
- Technological Homogenization: 90% of products still use the two-decade-old “sleeve heat exchanger + 304 stainless steel tank” solution.
- Overcapacity Crisis: Over 500 manufacturers nationwide operate at just 67% capacity utilization, with inventory turnover days reaching 142.
- Collapsing Profit Margins: The average winning bid price dropped from ¥3,800 in 2015 to ¥2,200 in 2025, with gross margins generally below 15%.
- Market Fragmentation: The top 5 brands hold only a 35% market share, while regional small factories survive relying on local protectionism.
3. Procurement Ecosystem: Deep-Seated Issues of Non-Market Operations
Distorted public procurement rules create systemic risks:
- Low-Price Bid Trap: In a 2024 provincial education department tender, 60% of bids weighted price at 50%, leading to inferior products entering schools.
- Strict Regional Barriers: A East China company relies on local government-business networks for 70% of its orders, with a cross-province bid success rate below 20%.
- Cost-Shifting Hazards: Some manufacturers substitute 201 stainless steel for 304, resulting in lead leaching levels 3 times exceeding the standard.
4. Consumer Perception: Cultural DNA and the Cognitive Gap
Drinking water safety anxiety shapes a unique market logic:
- Historical Imprint: The 1952 “Patriotic Health Campaign” established boiled water consumption as a national norm, deeply ingraining the concept of sterilization via boiling.
- Instant-Heating Trust Crisis: 75% of users refuse to drink unboiled RO water, even when TDS values are <10 ppm.
- Tank Risk Neglect: Only 30% of institutions perform monthly cleaning; long-term water storage leads to a 42% nitrite exceedance rate.
5. Driving Forces for Breakthrough: Policy and Technology as Twin Engines
- Policy Energy Efficiency Benchmarks:
- The 2025 “Public Institution Energy Conservation Regulations” mandate a 40% efficiency improvement for water dispensers, phasing out high-energy-consumption models.
- Guangdong Province’s “Green Home Appliance Subsidy” offers up to ¥500 per unit for energy-efficient dispensers.
- Technological Shift: Midea’s Shunde base will cease production of traditional tank models in 2025, pivoting to R&D for instant-heating modules.
Conclusion: A Historic Window for Innovation
As homogeneous competition and distorted procurement mire the industry in difficulty, policy upgrades and evolving consumer awareness are jointly prying open a new path. The shortcomings of traditional dispensers (“large and clumsy”) and instant-heating models (“unboiled”) pave the necessary way for the disruptive innovation of instant-boiling water solutions—a revolution redefining public drinking water is counting down.
Energy-efficient water dispenser, Public drinking water market, Instant-heating water dispenser, Drinking water safety, Energy efficiency standards, Price war, Homogeneous competition, Procurement ecosystem, Stainless steel water tank, RO reverse osmosis, Patriotic Health Campaign, Policy subsidies, Market penetration rate, Water quality standards, Innovation transformation





